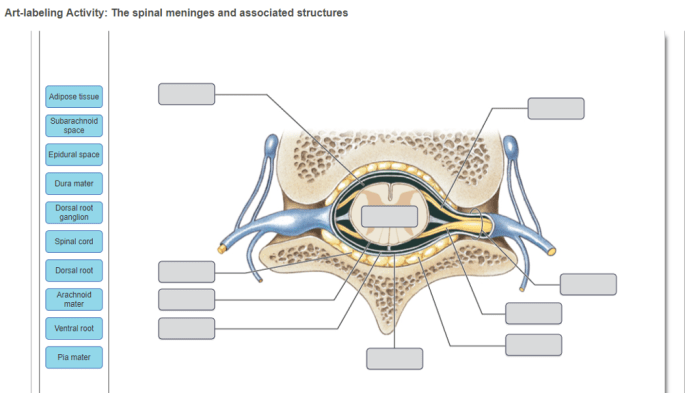
Art-labeling activity the spinal cord and spinal meninges – Embark on an engaging educational journey with our art-labeling activity on the spinal cord and spinal meninges. This immersive experience will illuminate the intricate anatomy and functions of these vital structures, providing a deeper understanding of their role in our body’s sensory and motor systems.
Delve into the fascinating world of neuroscience as we unravel the complexities of the spinal cord and its protective layers. Discover the different regions of the spinal cord and their specialized functions, and explore the crucial role of the spinal meninges in safeguarding this delicate structure.
The Spinal Cord
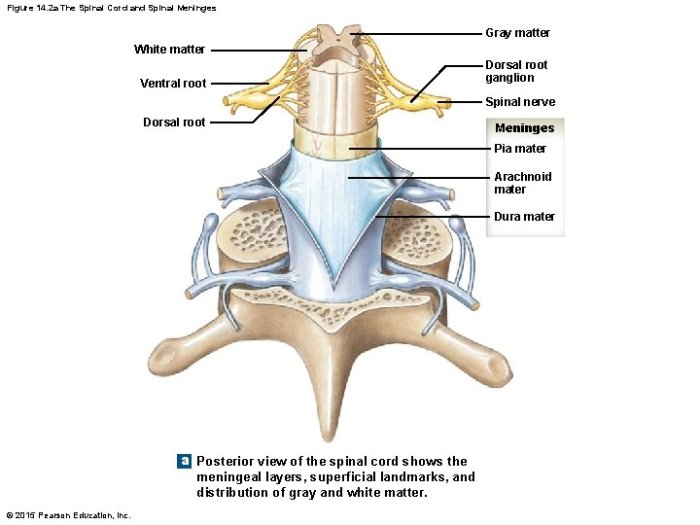
The spinal cord is a long, cylindrical bundle of nervous tissue that extends from the brainstem to the lower back. It is responsible for transmitting sensory and motor information between the brain and the rest of the body.
The spinal cord is divided into four regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral. The cervical region is located in the neck and contains the nerves that innervate the arms and hands. The thoracic region is located in the chest and contains the nerves that innervate the chest and abdomen.
The lumbar region is located in the lower back and contains the nerves that innervate the legs and feet. The sacral region is located at the bottom of the spinal cord and contains the nerves that innervate the pelvic organs.
The spinal cord is protected by the spinal meninges, which are three layers of connective tissue that surround the spinal cord and its roots.
The Spinal Meninges
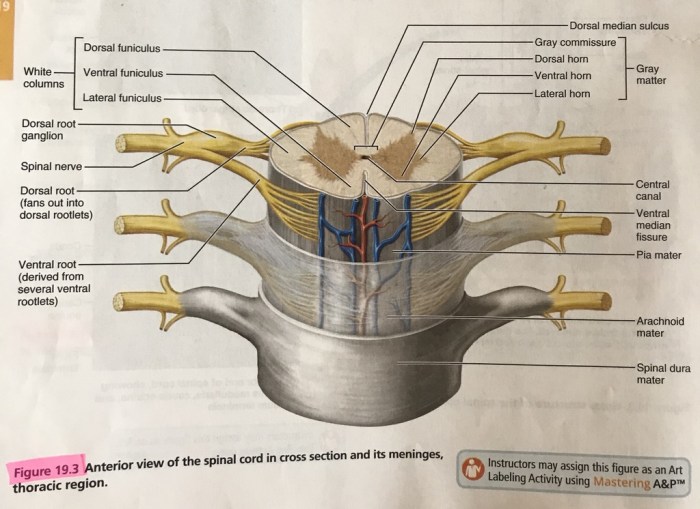
The spinal meninges are three layers of connective tissue that surround the spinal cord and its roots. The outermost layer is the dura mater, which is a tough, fibrous membrane. The middle layer is the arachnoid mater, which is a delicate, web-like membrane.
The innermost layer is the pia mater, which is a thin, vascular membrane that closely adheres to the surface of the spinal cord.
The spinal meninges serve several functions. The dura mater provides structural support and protection for the spinal cord. The arachnoid mater helps to cushion the spinal cord and provides a space for the cerebrospinal fluid to circulate. The pia mater provides a blood supply to the spinal cord and helps to anchor it to the vertebral column.
Art-Labeling Activity, Art-labeling activity the spinal cord and spinal meninges
Art-labeling activities are a great way to help students learn about the anatomy of the spinal cord and spinal meninges. To create an art-labeling activity, you will need to:
- Find an image of the spinal cord and spinal meninges.
- Label the different parts of the spinal cord and spinal meninges.
- Create a list of questions to guide students as they complete the activity.
Examples of Art-Labeling Activities
There are many different ways to create art-labeling activities. Here are a few examples:
- You can create a simple diagram of the spinal cord and spinal meninges and have students label the different parts.
- You can create a more complex diagram that includes additional information, such as the different regions of the spinal cord and the different types of nerve cells.
- You can create a three-dimensional model of the spinal cord and spinal meninges and have students label the different parts.
Helpful Answers: Art-labeling Activity The Spinal Cord And Spinal Meninges
What is the function of the spinal cord?
The spinal cord serves as a vital conduit for transmitting sensory and motor information between the brain and the rest of the body.
How many layers are there in the spinal meninges?
The spinal meninges consist of three layers: the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater.
What is the purpose of the art-labeling activity?
The art-labeling activity provides an engaging and interactive way to learn about the anatomy and functions of the spinal cord and spinal meninges.