Introducing the Periodic Table Vocabulary Worksheet Answer Key, your gateway to mastering the fundamental concepts of chemistry. This comprehensive guide empowers you to decipher the language of the periodic table, unlocking the secrets of the elements that shape our world.
Delve into the intricacies of atomic numbers, electron configurations, and periodic trends, gaining a profound understanding of how elements are organized and behave. With its interactive exercises and detailed explanations, this answer key transforms learning into an engaging and enlightening experience.
Vocabulary and Terminology: Periodic Table Vocabulary Worksheet Answer Key
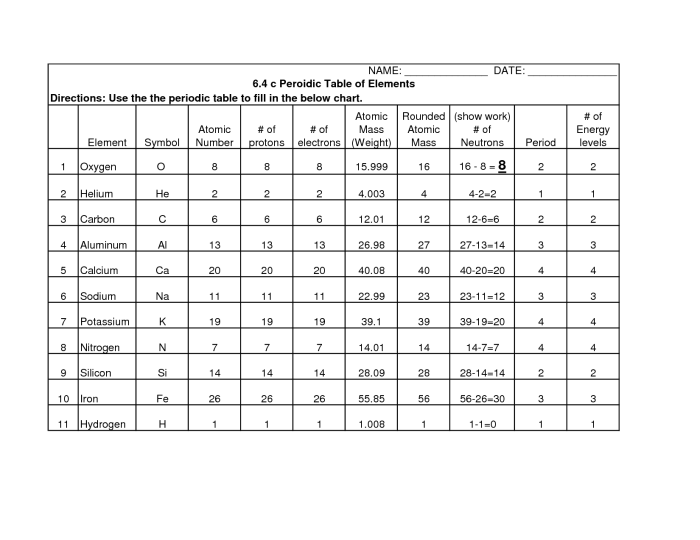
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. Understanding the key vocabulary and terminology associated with the periodic table is essential for comprehending its structure and the behavior of elements.
Glossary of Terms
- Atomic Number:The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, which determines the element’s identity.
- Atomic Mass:The weighted average mass of an element’s isotopes, expressed in atomic mass units (amu).
- Electron Configuration:The distribution of electrons in the atomic orbitals of an element.
- Period:A horizontal row in the periodic table, representing elements with the same number of electron shells.
- Group:A vertical column in the periodic table, representing elements with similar chemical properties due to having the same number of valence electrons.
- Valence Electrons:The electrons in the outermost shell of an atom, which determine its chemical reactivity.
- Periodic Trend:A regular pattern or change in the properties of elements as their atomic number increases.
Elements and their Properties
The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic number, which increases from left to right across the table. Elements in the same group share similar chemical properties, while elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells.
Atomic Number, Atomic Mass, and Electron Configuration, Periodic table vocabulary worksheet answer key
The atomic number of an element is unique to that element and determines its position in the periodic table. The atomic mass represents the average mass of an element’s isotopes, which are atoms of the same element with varying numbers of neutrons.
The electron configuration of an element describes the arrangement of its electrons in atomic orbitals. The number of valence electrons, which are the electrons in the outermost shell, determines an element’s chemical reactivity.
Periodic Trends
The periodic table exhibits several periodic trends, including:
- Metallic Character:Decreases from left to right across a period and increases from top to bottom within a group.
- Nonmetallic Character:Increases from left to right across a period and decreases from top to bottom within a group.
- Ionization Energy:The energy required to remove an electron from an atom, which generally increases from left to right across a period and decreases from top to bottom within a group.
- Electronegativity:The ability of an atom to attract electrons, which generally increases from left to right across a period and decreases from top to bottom within a group.
Groups and Periods

The periodic table is divided into 18 vertical groups (columns) and 7 horizontal periods (rows).
Groups (Vertical Columns)
Elements in the same group share similar chemical properties because they have the same number of valence electrons. For example, all elements in Group 1 (Alkali Metals) are highly reactive and form 1+ ions.
Periods (Horizontal Rows)
Elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells. As you move from left to right across a period, the atomic number and number of electrons increase, resulting in a gradual change in chemical properties.
Significance of Group and Period Numbers
The group and period numbers of an element provide valuable information about its properties:
- Group Number:Indicates the number of valence electrons and determines the element’s chemical reactivity.
- Period Number:Indicates the number of electron shells and influences the element’s size, ionization energy, and other properties.
FAQ Guide
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized by their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties.
Why is the periodic table important?
The periodic table provides a systematic framework for understanding the behavior and properties of elements, facilitating the prediction of their chemical reactions and applications.
What is the purpose of the Periodic Table Vocabulary Worksheet Answer Key?
The Periodic Table Vocabulary Worksheet Answer Key serves as a valuable resource for students, providing detailed explanations and solutions to the exercises in the worksheet, enhancing their understanding of periodic table concepts.