Phylogenetic Tree POGIL Answers Key: Unlocking the Secrets of Evolutionary History. Dive into the fascinating world of phylogenetic trees, where we unravel the intricate tapestry of life’s evolutionary journey. Through this comprehensive guide, you’ll gain access to a treasure trove of answers that illuminate the structure, construction, interpretation, and applications of phylogenetic trees.
Embark on an extraordinary voyage of discovery, where scientific rigor meets captivating storytelling.
Uncover the hierarchical organization of phylogenetic trees, deciphering the language of nodes and branches that reveal evolutionary relationships. Explore the diverse methods used to construct these intricate diagrams, delving into their advantages and limitations. Learn to interpret branch lengths, unraveling the mysteries of evolutionary distance.
Harness the power of bootstrap values, assessing the confidence of branching patterns with precision.
Phylogenetic Tree Structure: Phylogenetic Tree Pogil Answers Key
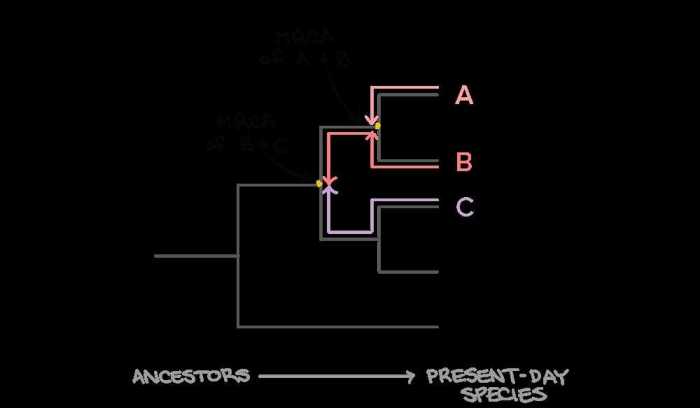
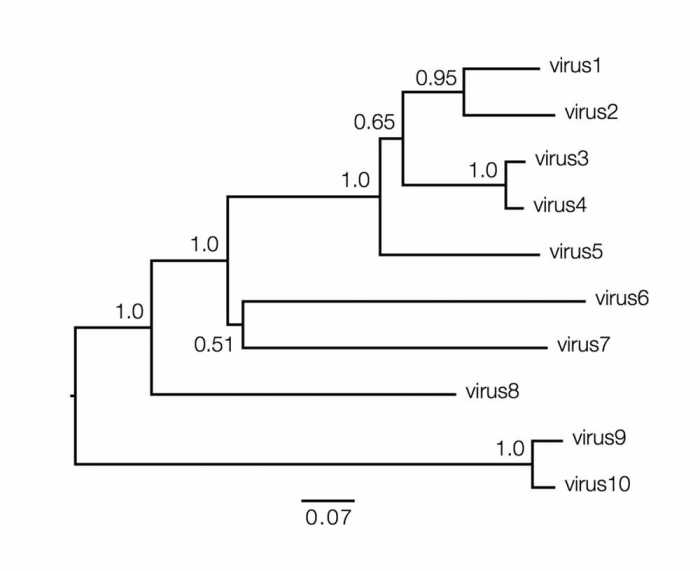
A phylogenetic tree is a diagram that represents the evolutionary relationships among different groups of organisms. It is a hierarchical structure that resembles a tree, with branches representing lineages and nodes representing common ancestors.
Each branch in a phylogenetic tree represents a period of evolutionary history, and the length of a branch is proportional to the amount of evolutionary change that has occurred along that lineage. Nodes in a phylogenetic tree represent common ancestors, and the branching pattern indicates the order in which different groups of organisms diverged from each other.
Phylogenetic trees provide a visual representation of the evolutionary history of a group of organisms, and they can be used to infer the relationships between different groups, as well as the timing and order of evolutionary events.
Phylogenetic Tree Construction Methods
There are several different methods that can be used to construct phylogenetic trees, including maximum parsimony, maximum likelihood, and Bayesian inference.
- Maximum parsimonyis a method that seeks to find the tree that requires the fewest evolutionary changes to explain the observed data. It is a relatively simple method to implement, but it can be computationally intensive for large datasets.
- Maximum likelihoodis a method that seeks to find the tree that is most likely to have produced the observed data. It is a more complex method than maximum parsimony, but it can be more accurate for large datasets.
- Bayesian inferenceis a method that uses Bayesian statistics to estimate the probability of different trees. It is a computationally intensive method, but it can be more accurate than maximum parsimony or maximum likelihood for complex datasets.
The choice of which method to use to construct a phylogenetic tree depends on the size and complexity of the dataset, as well as the computational resources available.
Interpreting Phylogenetic Trees
Phylogenetic trees can be interpreted to infer the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The branch lengths in a phylogenetic tree represent the amount of evolutionary change that has occurred along a particular lineage, and the branching pattern indicates the order in which different groups of organisms diverged from each other.
Bootstrap values are often used to assess the confidence of branching patterns in a phylogenetic tree. Bootstrap values represent the percentage of times that a particular branch was found in a set of bootstrap trees, which are trees that are constructed from resampled data.
Phylogenetic trees can be used to infer a variety of evolutionary events, such as speciation, extinction, and gene duplication. They can also be used to test hypotheses about the evolution of different traits.
Applications of Phylogenetic Trees
Phylogenetic trees have a wide range of applications in evolutionary biology, systematics, and comparative genomics.
- Evolutionary biology:Phylogenetic trees can be used to infer the evolutionary history of a group of organisms, including the timing and order of speciation and extinction events.
- Systematics:Phylogenetic trees are used to classify organisms into different groups, such as species, genera, and families. They can also be used to identify new species and to resolve taxonomic disputes.
- Comparative genomics:Phylogenetic trees can be used to compare the genomes of different organisms, and to identify genes and other genomic features that are conserved across species.
Phylogenetic Tree Limitations, Phylogenetic tree pogil answers key
Phylogenetic trees are a powerful tool for studying evolution, but they also have some limitations.
- Incomplete data:Phylogenetic trees are often constructed using incomplete data, which can lead to inaccurate or misleading results.
- Homoplasy:Homoplasy is the occurrence of similar traits in unrelated organisms due to convergent evolution. Homoplasy can make it difficult to construct accurate phylogenetic trees.
- Model selection:The choice of which model to use to construct a phylogenetic tree can affect the results. Different models can lead to different tree topologies.
Despite these limitations, phylogenetic trees are a valuable tool for studying evolution. They can provide insights into the evolutionary history of a group of organisms, and they can be used to test hypotheses about the evolution of different traits.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is a phylogenetic tree?
A phylogenetic tree is a diagram that represents the evolutionary relationships among different groups of organisms, depicting their common ancestry and divergence over time.
How are phylogenetic trees constructed?
Phylogenetic trees are constructed using various methods, including maximum parsimony, maximum likelihood, and Bayesian inference, each with its advantages and limitations.
What do the branch lengths in a phylogenetic tree represent?
Branch lengths in a phylogenetic tree represent the estimated evolutionary distance between organisms, with longer branches indicating greater evolutionary divergence.
How can phylogenetic trees be used?
Phylogenetic trees are used in various fields, including evolutionary biology, systematics, and comparative genomics, providing insights into evolutionary history, biodiversity, and the relationships between organisms.